Understanding Disinformation Understanding DisinformationDefinition of disinformation Click to read
|
Disinformation, misinformation and malinformation
Disinformation is false or misleading information that is intentionally spread with the purpose of deceiving or manipulating others.
Misinformation refers to false or inaccurate information that is spread without the deliberate intent to deceive. It can arise due to various reasons, such as misunderstanding, misinterpretation, or a lack of knowledge on the part of the person sharing the information.
Malinformation is true information that is shared with the explicit intent to cause harm, damage reputation, or invade privacy. It involves the deliberate disclosure of private or confidential information without consent, leaking sensitive documents, or sharing personal information to harm someone's reputation.
|

Source: https://firstdraftnews.org/long-form-article/understanding-information-disorder/
|
|
Type
|
Intent
|
Truthfulness of Information
|
Purpose
|
|
Disinformation
|
Intentional deception
|
False or misleading
|
Deceive, manipulate, shape public opinion
|
|
Misinformation
|
Unintentional dissemination
|
False or inaccurate
|
Lack of knowledge, misunderstanding
|
|
Malinformation
|
Deliberate harm
|
True
|
Cause harm, damage reputation, invade privacy
|
Types of disinformation Click to read
UNHCR (2022):
Fabricated Content: Completely false content;
Manipulated Content: Genuine information or imagery that has been distorted, e.g. a sensational headline or populist ‘click bait’;
Imposter Content: Impersonation of genuine sources, e.g. using the branding of an established agency;
Misleading Content: Misleading information, e.g. comment presented as fact;
False Context: Factually accurate content combined with false contextual information, e.g. when the headline of an article does not reflect the content;
Satire and Parody: Humorous but false stores passed off as true. There is no intention to harm but readers may be fooled;
False Connections: When headlines, visuals or captions do not support the content;
Sponsored Content: Advertising or PR disguised as editorial content;
Propaganda: Content used to manage attitudes, values and knowledge;
Error: A mistake made by established new agencies in their reporting.
Cheapfakes & deepfakes Click to read
|
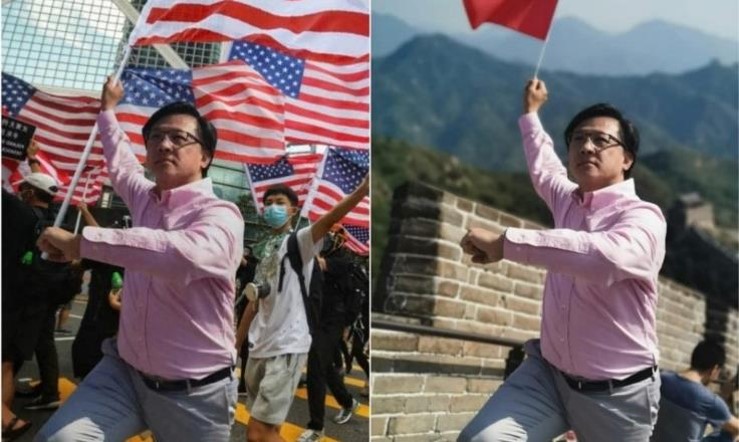
Cheapfakes refer to manipulated or edited media that are relatively simple and low-cost to create. They typically involve basic modifications to images or videos, such as adding or removing elements, altering context, or applying basic filters.
Deepfakes refer to highly realistic and sophisticated manipulated media that are created using deep learning algorithms and artificial intelligence (AI) techniques.
|

Deepfake created with Ai
|
Conspiracy Theories Click to read
Conspiracy theories are explanations or beliefs that propose a secretive, often nefarious, plot by a group of individuals or organizations to manipulate events or control certain outcomes. These theories typically involve allegations of hidden agendas, cover-ups, and collusion among powerful entities. Conspiracy theories often lack credible evidence and rely on speculation, misinterpretation, or fabrication of facts. They can cover a wide range of topics, from politics and government to health, science, and popular culture. Conspiracy theories can have significant social and psychological impacts, influencing public opinion, promoting distrust, and sometimes leading to harmful actions.
|
Conspiracy Theory
|
Description
|
|
9/11 Inside Job
|
Claims that the 9/11 attacks in the United States were orchestrated by the government to further political agendas or justify military actions.
|
|
Moon Landing Hoax
|
Suggests that the Apollo moon landings were faked by NASA as part of a larger conspiracy to deceive the public.
|
|
Illuminati Control
|
Alleges that a secret society called the Illuminati controls world events, governments, and major institutions to manipulate global affairs.
|
|
Chemtrails
|
Believes that airplane contrails are actually chemical or biological agents sprayed by the government for undisclosed purposes.
|
|
COVID-19 Bioweapon
|
Proposes that the COVID-19 pandemic was deliberately engineered or released as a bioweapon, rather than originating naturally.
|
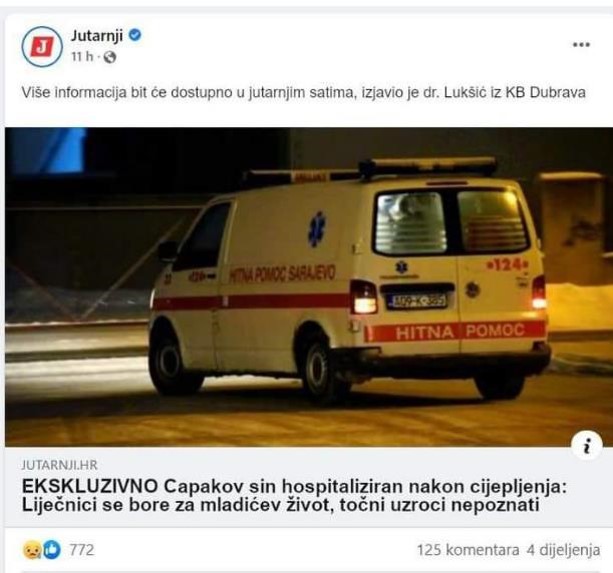
Fake news & pseudo media Click to read
Fake news refers to deliberately fabricated or misleading information presented as legitimate news. It can include false stories, manipulated images or videos, and misleading headlines that are spread through various channels, including social media, websites, and traditional media outlets. Fake news often aims to deceive or manipulate readers, provoke emotional responses, or advance specific agendas. It is important to critically evaluate sources and fact-check information to avoid falling for fake news and to promote the dissemination of accurate and reliable information.
Pseudo media are media outlets or platforms that engage in deceptive or misleading practices, presenting themselves as legitimate sources of news or information while lacking journalistic integrity or adhering to ethical standards. Pseudo media might intentionally disseminate false or biased information, manipulate facts, or engage in sensationalism to attract attention or promote certain narratives.
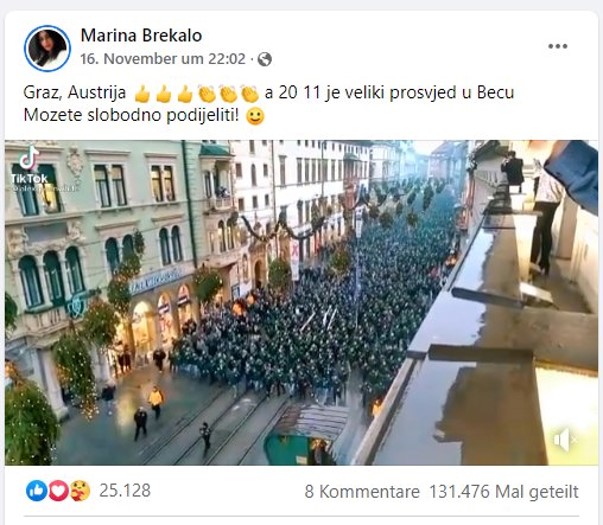
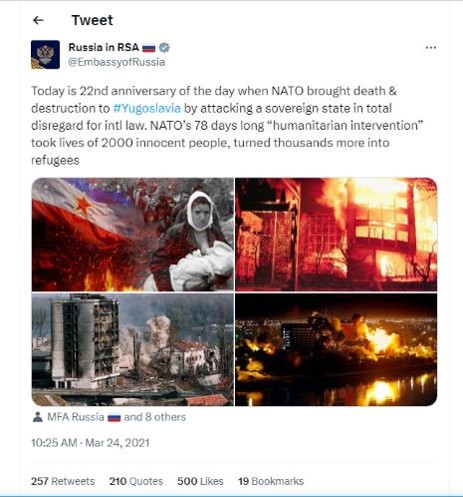
The motives behind disinformation Click to read
Political Manipulation: Disinformation can be used to manipulate public opinion, influence elections, or shape political narratives in favor of a particular candidate, party, or ideology. It aims to sow discord, undermine trust in democratic processes, or advance geopolitical interests.
Propaganda and Ideology: Disinformation can be employed to promote a specific ideology, advance propaganda agendas, or support extremist or separatist movements. It aims to shape perceptions, recruit supporters, or demonize opposing groups.
Economic Gain: Disinformation can be motivated by financial incentives. Individuals or groups may spread false information to drive traffic to their websites, increase ad revenue, or promote products or services based on deceptive claims.
Social Division and Polarization: Disinformation can exploit societal fault lines, exacerbate existing tensions, and deepen social divisions. By amplifying controversial or divisive issues, it aims to foster mistrust, create animosity, and undermine social cohesion.
Personal or Organizational Reputation: Disinformation can be used to tarnish the reputation of individuals, organizations, or institutions. It aims to damage credibility, undermine trust, or settle personal or professional rivalries.
State-Sponsored Influence: Disinformation campaigns can be orchestrated by nation-states to achieve strategic objectives. This may include spreading false narratives to destabilize rival nations, manipulate global perception, or advance foreign policy goals.
Veles story
|
Economic Gain
Teenagers in Veles, Macedonia used disinformation to create fake news websites, aiming to generate ad revenue. They produced sensationalized stories favoring Donald Trump, which gained significant social media traction. While the impact on the 2016 US elections is debated, it highlighted the vulnerability of online information ecosystems to manipulation.
|

Source: https://money.cnn.com/interactive/media/the-macedonia-story/
|
Impact on the society Click to read
Key ways in which disinformation can affect society:
|
Impact
|
Description
|
|
Undermining Trust
|
Erodes trust in institutions, media, and public figures, making it harder to discern between accurate and false information.
|
|
Polarization and Divisiveness
|
Exploits divisions, fosters animosity, and contributes to social polarization and unrest.
|
|
Manipulating Public Opinion
|
Shapes narratives, distorts public perceptions, and influences elections and policy decisions.
|
|
Public Health and Safety
|
Endangers public health by spreading false information about medical treatments, vaccines, and public health emergencies.
|
|
Economic Impact
|
Harms businesses and markets through false information affecting reputation, stock prices, and consumer behaviour.
|
|
Personal and Social Consequences
|
Damages individual reputations, spreads false accusations, and contributes to psychological distress and social cohesion erosion.
|
|
Misallocation of Resources
|
Wastes resources on debunking false claims, investigating fake news sources, and implementing measures to counter disinformation.
|
|
Threats to Democracy
|
Undermines democratic processes by manipulating information and potentially influencing election outcomes.
|
Example of Capitol Hill siege
|
Trump fans fueled US Capitol takeover
Disinformation played a significant role in the Capitol Hill siege on January 6, 2021. False election claims, conspiracy theories, and misattributions to Antifa and BLM fueled the belief that the election was stolen, radicalizing individuals. Extremist views were amplified, leading to the organization and coordination of the attack. Dissemination of false narratives downplayed the violent intent. The incident underscored the dangerous consequences of disinformation, highlighting its ability to incite real-world harm and undermine democratic processes.
|
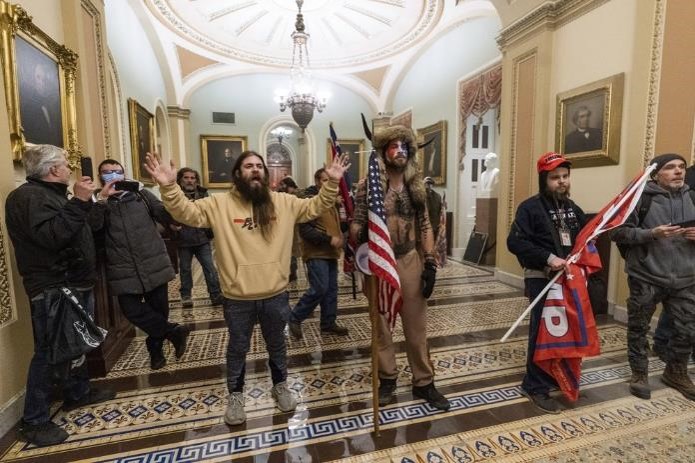

Source: https://apnews.com/article/us-capitol-trump-supporters-1806ea8dc15a2c04f2a68acd6b55cace
|
The role of social media Click to read
Social media plays a significant role in the sharing of disinformation. Its ease of use and wide reach make it a breeding ground for the rapid spread of false or misleading information. Social media platforms amplify and disseminate misinformation through user-generated content, fake accounts, and algorithmic biases. The viral nature of sharing on social media can quickly amplify disinformation, leading to the erosion of trust, polarization of opinions, and potential real-world consequences.
From October 1 to December 31, 2022, the number of different posts on Facebook that received disinformation labels after being assessed for falsehood by fact-checking organizations.
|
Country
|
Facebook*
|
Instagram*
|
|
Austria
|
Over 660.000
|
Over 46.000
|
|
Belgium
|
Over 990.000
|
Over 66.000
|
|
Bulgaria
|
Over 510.000
|
Over 18.000
|
|
Croatia
|
Over 410.000
|
Over 21.000
|
|
Cyprus
|
Over 189.000
|
Over 21.000
|
|
Czech Republic
|
Over 600.000
|
Over 30.000
|
|
Denmark
|
Over 410.000
|
Over 33.000
|
|
Estonia
|
Over 77.000
|
Over 9.900
|
|
Finland
|
Over 180.000
|
Over 30.000
|
|
France
|
Over 4.000.000
|
Over 150.000
|
|
Germany
|
Over 3.700.000
|
Over 210.000
|
|
Greece
|
Over 860.000
|
Over 42.000
|
|
Hungary
|
Over 450.000
|
Over 21.000
|
|
Ireland
|
Over 580.000
|
Over 80.000
|
|
Italy
|
Over 4.000.000
|
Over 170.000
|
|
Latvia
|
Over 180.000
|
Over 10.000
|
|
Lithuania
|
Over 210.000
|
Over 11.000
|
|
Luxembourg
|
Over 97.000
|
Over 12.000
|
|
Malta
|
Over 81.000
|
Over 9.200
|
|
Netherlands
|
Over 1.000.000
|
Over 104.000
|
|
Poland
|
Over 1.700.000
|
Over 52.000
|
|
Portugal
|
Over 1.600.000
|
Over 240.000
|
|
Romania
|
Over 1.100.000
|
Over 34.000
|
|
Slovakia
|
Over 360.000
|
Over 17.000
|
|
Slovenia
|
Over 220.000
|
Over 12.000
|
|
Spain
|
Over 3.500.000
|
Over 200.000
|
|
Sweden
|
Over 620.000
|
Over 69.000
|
|
Total EU
|
Over 28.000.000
|
Over 1.700.000
|
Source: https://disinfocode.eu
|
The trumpet of amplification
The diagram illustrates the path disinformation often takes, starting from anonymous web platforms, moving through closed groups, conspiracy communities, and eventually reaching open social networks and professional media. Disinformation agents aim to amplify their message, and unfortunately, they often succeed when false information is embedded in news articles.
|

Source: https://firstdraftnews.org/articles/5-lessons-for-reporting-in-an-age-of-disinformation/
|
The fact-checking organizations Click to read
Fact-checking organizations are independent entities dedicated to assessing the accuracy and veracity of claims made in public discourse, particularly in the media and online platforms. They employ journalists, researchers, and subject matter experts to investigate claims, analyze evidence, and provide objective evaluations. Fact-checkers utilize various methods, such as sourcing reliable information, conducting interviews, and analyzing data, to determine the validity of statements. Some well-known fact-checking organizations include PolitiFact, Snopes, FactCheck.org, AFP Fact Check, Full Fact, and The Washington Post's Fact Checker. These organizations play a crucial role in promoting truth and combating the spread of misinformation.
The list of fact-checking organisations https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_fact-checking_websites
|
International Fact-Checking Network
The International Fact-Checking Network (IFCN) is a vital global organization that promotes accuracy and accountability in journalism. It sets standards for fact-checking organizations, offers training and resources, and facilitates the sharing of best practices. The IFCN also certifies fact-checkers through the transparent process of the IFCN Code of Principles. In parallel, the European Fact-Checking Standards Network Project, an EU initiative, brings independent fact-checking organizations together to define standards of independence, transparency, and journalistic quality in combating disinformation. These combined efforts enhance information quality and foster public trust in the media.
|
 |
|
Meta (Facebook) and fact-checkers
Meta works with certified independent fact-checkers from the International Fact-Checking Network to combat disinformation. They work independently to review and evaluate potential disinformation on Meta's platforms. More than 90 organizations in 60 languages participate and take action against viral hoaxes and false claims. Meta and the fact checkers work together in three ways: Identifying potential disinformation, reviewing and evaluating the accuracy of content, and taking action. When content is determined to be false, its distribution is significantly restricted, warning labels are posted, and people are notified. Meta's three-part approach is to remove, reduce and inform about problematic content. Fact-checking partners adhere to IFCN's Code of Principles.
|
 |
 Identifying Disinformation Identifying DisinformationHow to recognizing disinformation? Click to read
Recognizing disinformation can be challenging, as it often appears realistic and is disseminated widely. To analyze and identify disinformation, follow these steps:
- Check the source for credibility and check the URLs.
- Look beyond the headline and watch for grammatical errors and inconsistencies.
- Distinguish between satire and factual content.
- Check references in the story and their credibility.
- Be aware of your personal bias and look at facts objectively.
Source: https://yali.state.gov/how-to-spot-disinformation/
|
Strange URL
|
Example Website
|
|
abcnews.com.co
|
Fake news site posing as ABC News
|
|
cnn-trending.com
|
Fake news site imitating CNN
|
|
nytimes.com.co
|
Fake news site mimicking The New York Times
|
|
bbc-news.co.uk
|
Fake news site resembling BBC News
|
|
washingtonpost.com.co
|
Fake news site pretending to be The Washington Post
|
|
huffingtonpost.com.co
|
Fake news site masquerading as The Huffington Post
|
|
fox-news24.com
|
Fake news site imitating Fox News
|
|
nbcnews.com.co
|
Fake news site mimicking NBC News
|
|
usatoday.com.co
|
Fake news site posing as USA Today
|
|
time-news.net
|
Fake news site resembling Time Magazine
|
How do I know if a source is credible?
- Look for content written by authoritative authors or reputable publishers, such as recognized experts in the field or well-established media outlets like the NY Times or Wall Street Journal.
- Check for proper citations or references to reliable sources used in the content, ensuring transparency and the ability to verify the information provided.
- Seek up-to-date information on your topic, as it reflects the most current understanding and knowledge surrounding the subject matter.
- Ensure the content presents an unbiased analysis of the topic, where the author explores multiple perspectives and considers various viewpoints rather than favoring a particular stance.
Red flags of disinformation Click to read
|
Red Flags of Misinformation
|
Description
|
|
Lack of credible sources
|
Claims without credible sources should raise suspicion and indicate potential disinformation.
|
|
Emotional content
|
Disinformation often evokes strong emotions to manipulate readers. Be cautious when encountering emotionally charged posts.
|
|
Cross-posted content
|
Disinformers spread false information by sharing it across multiple social platforms. Watch out for content shared across platforms.
|
|
Disinformation in memes
|
Memes, while entertaining, can also be a source of disinformation. Be cautious and fact-check before sharing memes.
|
 |
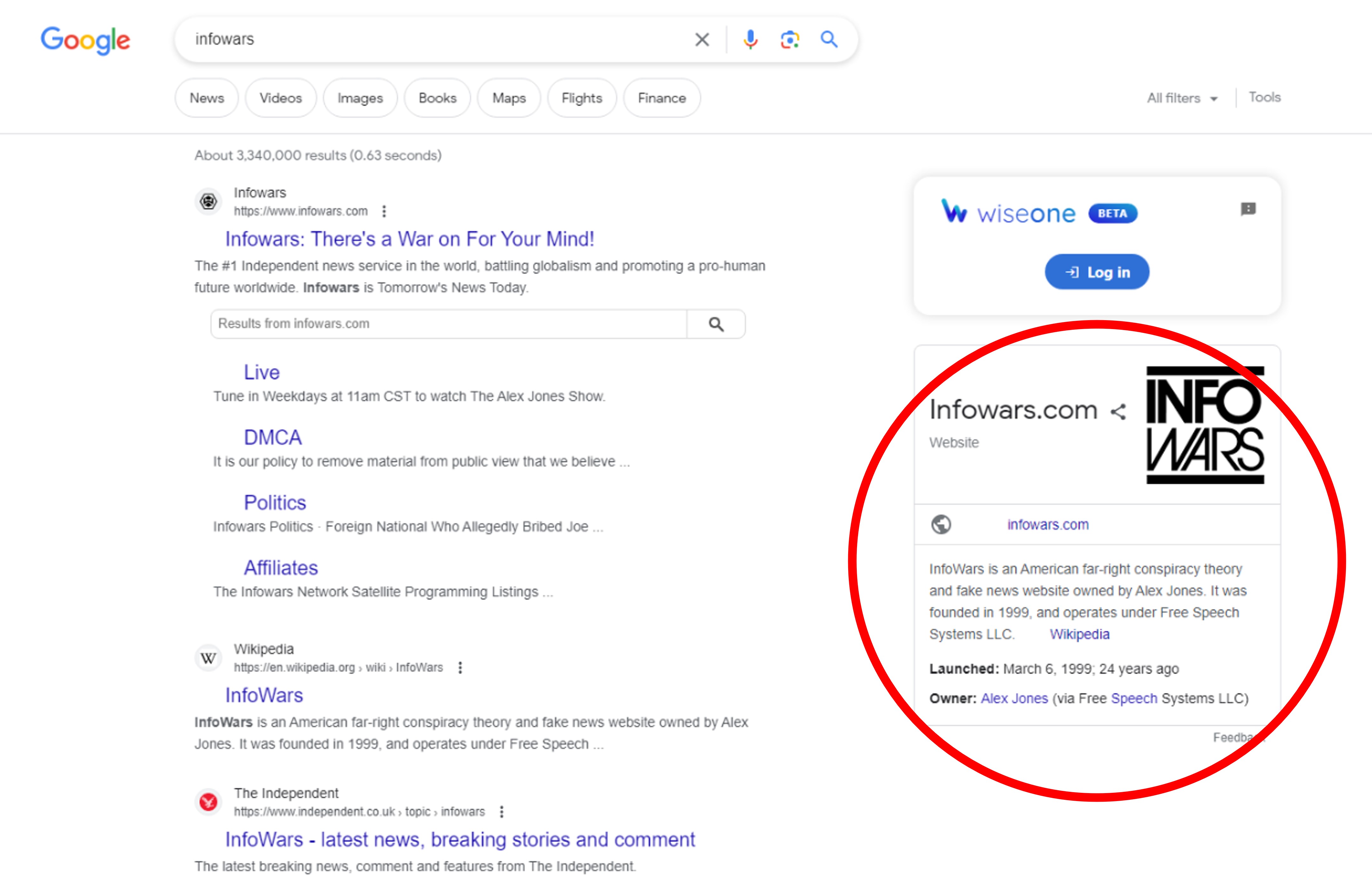
Check the domain name - Inforwars
Check the author –N/a
Check the date – January 2, 2022
Check the claims and access the sources the article reference
Read the article https://www.infowars.com/posts/australia-admits-widespread-severe-adverse-reactions-from-covid-jab-already-making-compensation-payments/
Watch the video mentioned in the article
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BzUSjTsjcac
Analysis:
Headline use „sever adverse” but referenced video use only „adverse”
Text:
„ 7News Australia reported on Friday that as much as 79,000 people have suffered from severe side effects from the COVID jab, and the government is prepared to dole out over $600,000 in compensation for some victims.”
Reference video report:
„It’s estimated that 79,000 people have suffered adverse reactions to vaccines. Now the government’s offering compensation. Claims under $20,000 will need evidence from your doctor. Claims over $20,000 assessed by a team of legal experts. The highest figure reserved for only the most serious of cases”
„adverse" typically refers to something harmful, unfavorable, or detrimental, while "severe" indicates something intense, serious, or extreme.
Fact-check https://seecheck.org/index.php/2022/01/19/no-79000-severe-reactions-to-covid-19-vaccines-have-been-reported-in-australia/
|
Fact-checking tools Click to read
|
Ordinary citizens have access to several fact-checking tools that can help them verify information and identify potential disinformation. One popular tool is "FactCheck.org," which provides unbiased analysis of political claims and news articles. "Snopes" is another well-known platform that verifies urban legends, rumors and misinformation. To verify content on social media, tools like "Google Reverse Image Search" can help determine the authenticity of images. In addition, browser extensions such as "NewsGuard" provide credibility ratings for websites that flag unreliable sources. Citizens can also consult reliable news outlets and use fact-checking databases such as "PolitiFact," "The Washington Post's "Fact Checker," or "AP Fact Check" to obtain accurate information. By using these tools, citizens can actively participate in the fight against disinformation and promote informed discussions.
The list of the tools: https://www.rand.org/research/projects/truth-decay/fighting-disinformation/search.html
|
 |
 Responsible Online Behavior Responsible Online BehaviorRecognize your cognitive biases Click to read
Cognitive biases are inherent tendencies in our thinking that can lead to errors in judgment. It is crucial for older adults to be aware of these biases when navigating the online world. Some common cognitive biases include confirmation bias (favoring information that confirms preexisting beliefs), availability bias (relying on readily available information), and anchoring bias (being influenced by initial information received). Recognizing these biases can help older individuals approach online content with a critical mindset and avoid being easily swayed by misleading information.
Recognize signs of cognitive bias
- You pay attention only to news that confirms your opinion
- You blame external factors when things do not go your way
- Attributing other people's success to luck, while taking credit for your own achievements
- Assuming that everyone else shares your opinions or beliefs
- Learning a little about a subject and then assuming you know everything about it
Build resilience to disinformation Click to read
In order to navigate the online world responsibly, there are key steps to follow. First, verify information by fact-checking it before believing or sharing. Seek reliable sources and consult reputable fact-checking organizations, while cross-referencing information to ensure accuracy. Second, be mindful of emotional triggers that disinformation often exploits. Stay aware of content that evokes strong emotions and take a step back to evaluate credibility, considering alternative perspectives before reacting or sharing. Third, develop a critical eye when consuming online content by scrutinizing sources, checking for supporting evidence, and questioning claims that seem too good to be true or lack sufficient evidence. Lastly, seek out diverse perspectives to gain a well-rounded understanding, engaging with reputable news outlets, expert opinions, and alternative viewpoints to avoid falling into echo chambers and being swayed by one-sided narratives.
6 steps to responsible online behaviour Click to read
- Verify before sharing: Check the authenticity and credibility of information against reliable sources or fact-checking organizations before sharing.
- Diversify your sources: Rely on multiple trusted sources for news and information to avoid bias and misinformation. Follow reputable news outlets, fact-checking websites, and experts in various fields.
- Question and analyze: Develop a critical mindset by questioning the information you come across. Evaluate the source, examine the evidence presented, and assess possible biases or conflicts of interest.
- Use fact-checking tools: Use fact-checking tools and resources available online to verify the accuracy of claims and statements.
- Be aware of emotional triggers: Disinformation often aims to evoke strong emotions. Be aware of emotional triggers and take a moment to think before responding or sharing. Emotional reactions can cloud judgment and contribute to the spread of misinformation.
- Report and flag disinformation: If you come across false or misleading information, report it to the platform or social media site where you found it.
Summing up Click to read
|
Well done! Now you know more about:
 Disinformation as deliberately false information aimed at deceiving or manipulating people, with far-reaching and detrimental effects on society. Disinformation as deliberately false information aimed at deceiving or manipulating people, with far-reaching and detrimental effects on society.
 The consequences of disinformation that can cause confusion, undermine confidence, and hinder informed decision making, especially for those in the 60+ age group. The consequences of disinformation that can cause confusion, undermine confidence, and hinder informed decision making, especially for those in the 60+ age group.
 The importance of fact-checking information, the role of emotional triggers, critically evaluating content, and seeking different perspectives to navigate the online world responsibly. The importance of fact-checking information, the role of emotional triggers, critically evaluating content, and seeking different perspectives to navigate the online world responsibly.
|
 |
|
 Understanding Disinformation
Understanding Disinformation Identifying Disinformation
Identifying Disinformation Responsible Online Behavior
Responsible Online Behavior